
Outlook for Manufacturing Industry:

CDIO,
JK Tyre & Industries
Some of the dust has begun to settle for the manufacturing sector following the severe volatility of 2020, but that doesn’t mean either is returning to how they looked before the pandemic began. The manufacturing industry looks for ways to make itself disruption-proof with a commitment to increase agility in operations. By continuing to invest in digital initiatives across their production process and supply network, manufacturers can respond to the disruptions caused by the pandemic and build resilience that can enable them to thrive. Manufacturers are required to be closer to their customers and to adopt tech-enabled distributed manufacturing solutions.
Outlook for Automotive & Tyre Industry:
As the industry is evolving with newer technologies such as Industry 4.0, use of AI and digitalisation, the landscape in the automotive industry is changing as well. The major thrust is towards making the automotive industry far safer and environment friendly. Similarly, the tyre industry is continuously enhancing capabilities, on the one hand to meet the emerging and stringent requirements posed by the automotive industry and, on the other hand, making all-out efforts towards environment protection, durability and safety.
Some key areas in technology growth are towards low rolling resistance, lower noise and excellent ride and handling, coupled with the challenges of EV Mobility and use of sensor technology for safer and fuel-efficient driving. Hence, the technology will continuously change the landscape in the future. The industry is spending almost 1.5 per cent of its turnover on R&D activities to ensure cutting edge technology is available to their consumers.
Tyre sector seems to ride through the downturn successfully. Currently, things are looking up for the auto sector in India after two years of a downward spiral. The growth in tyre demand is expected to be in sync with the economic and auto sector’s growth. The new vehicle scrappage policy is a welcome move, since it is aimed at phasing out unfit and polluting vehicles from the roads. Such a policy, with in-built incentives, will boost the demand for new and environment-friendly vehicles.
Industry 4.0:
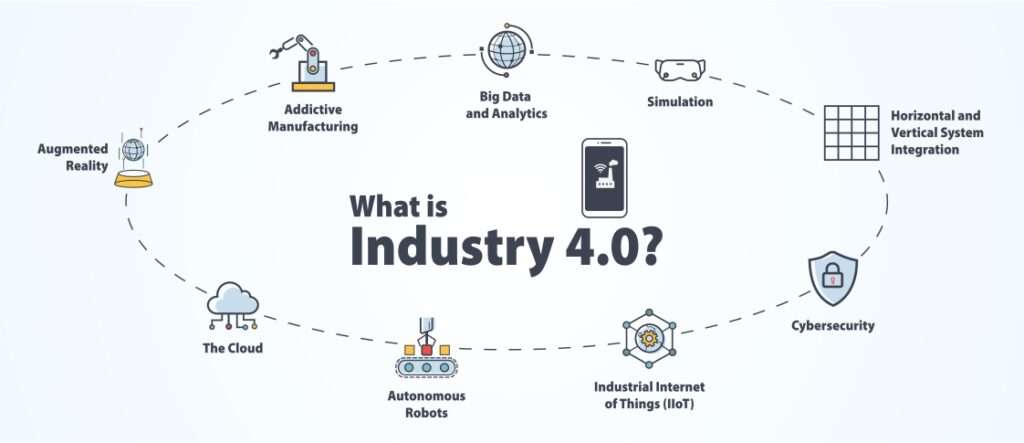
Industry 4.0, or the Fourth Industrial Revolution, takes automation of manufacturing processes to a higher level with smart autonomous systems capable of self-cognition, self-optimization, and self-customization. Industry 4.0 includes concepts, tools and applications that complement a smart embedded system of machines able to communicate with each other and people and perform autonomous tasks in industrial production processes.
 Source: PD Solutions
Source: PD Solutions
The main tools include cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things, big data and cloud computing, autonomous robots, simulation and visualization models, and additive manufacturing. Automation and Robotics are perceived as key components – the arms and legs – of Industry 4.0; cameras and other sensors are perceived as the senses; data and connectivity are compared to the nervous system; and artificial intelligence (AI) is the brain. It is bringing about a paradigm shift that will profoundly change the way we work, live and interact.
Challenges of Industry 4.0:
- Outdated international rules and regulations
- Standards and interoperability
- Data ownership and security
- Intellectual property protection
- Reliability and stability of cyber-physical systems
- Transparency, privacy, ethics and security
- Infrastructure gaps
- Inequality and exclusion coupled with barriers to entry
Opportunities of Industry 4.0:
- Economic gains because of lower transaction costs
- More reliable and consistent productivity and output with better quality products
- Enabling innovation across many applications
- Energy-efficient and environmentally sustainable production and systems
- Effective use of human and material resources
- Improvements in the health and safety of workers
- Changes in education and training systems
- Changes in the organization of work, with more remote, flexible and on-demand work becoming a standard
Factory of the future – Era of intelligent and connected plants
Today’s plants are getting transformed into intelligent and connected plants with advanced man-machine interface. The high-tech solutions are finding applications across various stages of the value chain e.g., engineering, testing, production planning and services.

Next Generation Smart Factories of the World will be characterized by advanced Machine to Machine and Man to Machine communications through sensors, identifiers and platforms to achieve constant connectivity between man, machines, equipment and tools.
The next major transition will be to the “autonomous” i.e., the fully automated “lights out factory”. Such a factory however is expected to require extensive automation and networking of the manufacturing processes, enabling the ultimate shift to a fully connected enterprise.
Age of connected cars & telematics – Evolution of software-enabled OEMs
Vehicles with connected features have seen a rising trend across the globe as the data network and internet reach have been widening. The connected vehicles and telematics solutions offer several entertainment, convenience, usage (operational metrics) and safety features. The connected vehicle fleet size across they key regions of U.S., Europe and China is expected to reach ~450 million units by 2025 and further grow to ~700 million units by 2030. Although the penetration of connected cars is relatively low in emerging markets like India, the Indian market has been witnessing a rise in demand for connectivity and telematics solutions.
Similar to the other internet connected devices, connected cars and connected vehicles face risks from various cyber criminals. The security violations and breaches can result in leakage of data, creating safety and security threats for the users. With enhancement in the level of autonomy and connectivity, the risks are expected to grow multifold in future. It will be needed to leverage the real-time data fetched from on-road connected vehicles to come up with innovative secured solutions.
In addition to the connectivity features for individual customers, fleet telematics solutions have also been gaining traction. The fleet operators are using telematics solutions to drive productivity and utilization while ensuring safety of the vehicles. Telematics solutions are increasingly being adopted by the new-age fleet aggregators, which are focused on driving up the overall run-time and utilization of their fleet.
Key challenges and way forward
Although industry 4.0 offers a myriad of benefits, the adoption of these new-age technologies has been relatively limited in India when compared to developed countries. Low understanding of the business impact, unavailability of cost-effective solutions and shortage of requisite capital/ talent pool are some of the major deterrents for Industry 4.0 adoption. Investments and collaborations among industry, academia and Government will hence be needed to enable requisite ecosystem and talent pool.
About the author
Sharad Kumar Agarwal comes with over 27 years of proven cross functional expertise in the fields of IT & Business Management with a penchant for knowledge, learning and market awareness. Currently, the CDIO at JK Tyre & Industries Ltd, Sharad has strong domain experience in Manufacturing covering the entire gamut of Production, Maintenance, Quality, Projects, Technical & Service functions. An effective communicator with excellent relationship management and team handling skills. believes that the mantra for success is to deliver technology led sustained results with effective change management.





