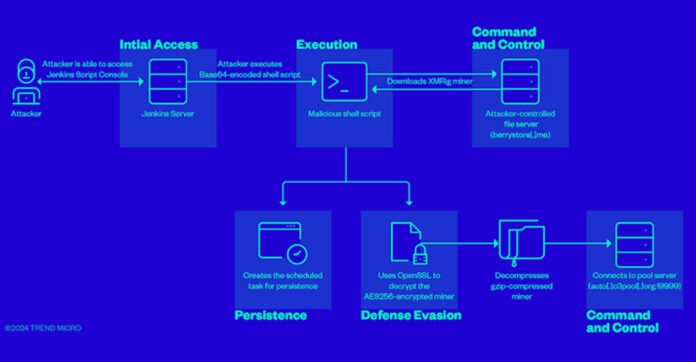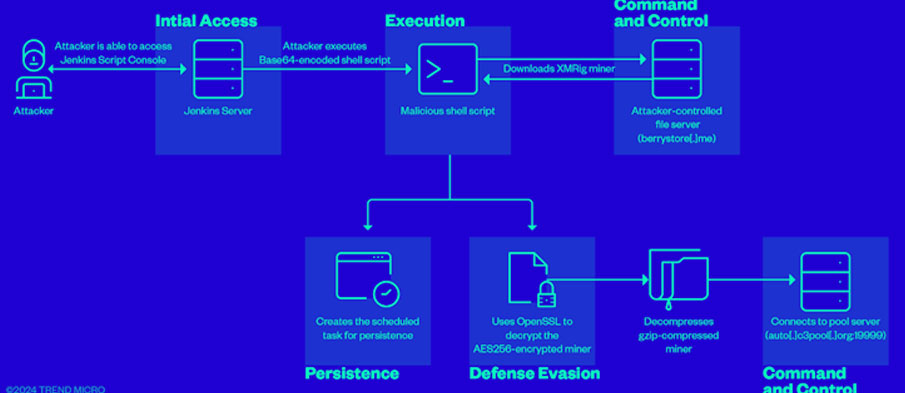
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered that attackers can exploit improperly configured Jenkins Script Console instances to carry out criminal activities such as cryptocurrency mining.
“Misconfigurations, like improperly set up authentication mechanisms, expose the ‘/script’ endpoint to attackers,” Trend Micro’s Shubham Singh and Sunil Bharti explained in a technical write-up published last week. “This can lead to remote code execution (RCE) and misuse by malicious actors.”
Jenkins, a popular continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform, includes a Groovy script console that allows users to run arbitrary Groovy scripts within the Jenkins controller runtime.
According to the project’s official documentation, the web-based Groovy shell can be used to read files containing sensitive data (e.g., “/etc/passwd”), decrypt credentials configured within Jenkins, and even reconfigure security settings.
The console “offers no administrative controls to stop a user (or admin) once they are able to execute the Script Console from affecting all parts of the Jenkins infrastructure,” the documentation states. “Granting a normal Jenkins user Script Console Access is essentially the same as giving them Administrator rights within Jenkins.”
While access to the Script Console is typically limited to authenticated users with administrative permissions, misconfigured Jenkins instances could inadvertently expose the “/script” (or “/scriptText”) endpoint to the internet, making it vulnerable to exploitation by attackers looking to run harmful commands.
Trend Micro reported finding instances of threat actors exploiting the Jenkins Groovy plugin misconfiguration to execute a Base64-encoded string containing a malicious script designed to mine cryptocurrency on the compromised server. This was done by deploying a miner payload hosted on berrystore[.]me and setting up persistence.
“The script ensures it has enough system resources to perform the mining effectively,” the researchers noted. “To do this, the script checks for processes that consume more than 90% of the CPU’s resources and then proceeds to kill these processes. Additionally, it will terminate all stopped processes.”
To protect against such exploitation attempts, it is advised to ensure proper configuration, implement robust authentication and authorization, conduct regular audits, and restrict Jenkins servers from being publicly exposed on the internet.
This development comes as cryptocurrency thefts from hacks and exploits have surged in the first half of 2024, allowing threat actors to steal $1.38 billion, up from $657 million year-over-year.
“The top five hacks and exploits accounted for 70% of the total amount stolen so far this year,” stated blockchain intelligence platform TRM Labs. “Private key and seed phrase compromises remain a top attack vector in 2024, alongside smart contract exploits and flash loan attacks.”